California is the first state in the nation to establish a system of MPAs – similar to national parks and forests on land – to protect and restore ocean habitats and increase the health, productivity, and resilience of ocean ecosystems. Under the California Marine Life Protection Act (MLPA) passed in 1999, California took a regional approach to the design and implementation of MPAs along its 1,100 mile coastline, and divided the state into five regions: the north coast, north central coast, central coast, south coast and San Francisco Bay. The state completed the coastal network of MPAs in 2012, creating over 120 underwater refuges along California’s coast, extending from Oregon to Mexico. For more information, download California Department of Fish and Wildlife’s Marine Protected Area Online Resources sheet.

California State MPAs
Types of MPAs
Marine Protected Areas come in all types of shapes, sizes, and purposes. As the coastal resources are a public trust, it is necessary to balance needs for multiple use with conservation priorities. The MLPA provides for this by defining four different types of MPAs:
- State Marine Reserves (SMR)
These restrict all commercial and recreational activities, keeping the area as free from human impact as possible. - State Marine Conservation Areas (SMCA)
These are areas that have specific goals for conservation and activities are restricted to meet the conservation goals. - State Marine Parks (SMP)
These allow opportunities for education, research, and recreation, while preventing commercial extractive activities. - State Marine Recreational Management Areas (SMRMA)
These are areas intended to protect certain recreational activities. Other types of activities that may interfere or compete with the specifically protected recreation are restricted. - Special Closures
Special Closures are areas designated by the Fish and Game Commission that prohibit access or restrict boating activities in waters adjacent to sea bird rookeries or marine mammal haul-out sites (restrictions vary).
Implementing the MLPA: A Stakeholder Process
The MLPA process was a stakeholder driven process that used the best readily available science to design a network of MPAs that spans the entire California coast. The goals (14K PDF file) of this network are to: 1) conserve key marine habitats, 2) allow marine life to thrive, 3) preserve natural diversity, 4) help rebuild depleted populations, and 5) offer recreational, research, and economic opportunities.
- Integration of California’s Marine Protected Areas: Review and Recommendations (2.6M PDF file)
Ocean Conservancy – Samantha Murray and Gia Brazil
The goal of this document is to capture MPA integration insights and lessons learned across key agencies and identify trends, examples and best practices used to assess project impacts and uphold MPA protections.
A Regional Process
California took a regional approach to the design and implementation of MPAs along its 1,100 mile coastline, and divided the state into five study regions: the north coast, south coast, north central coast, central coast and San Francisco Bay.
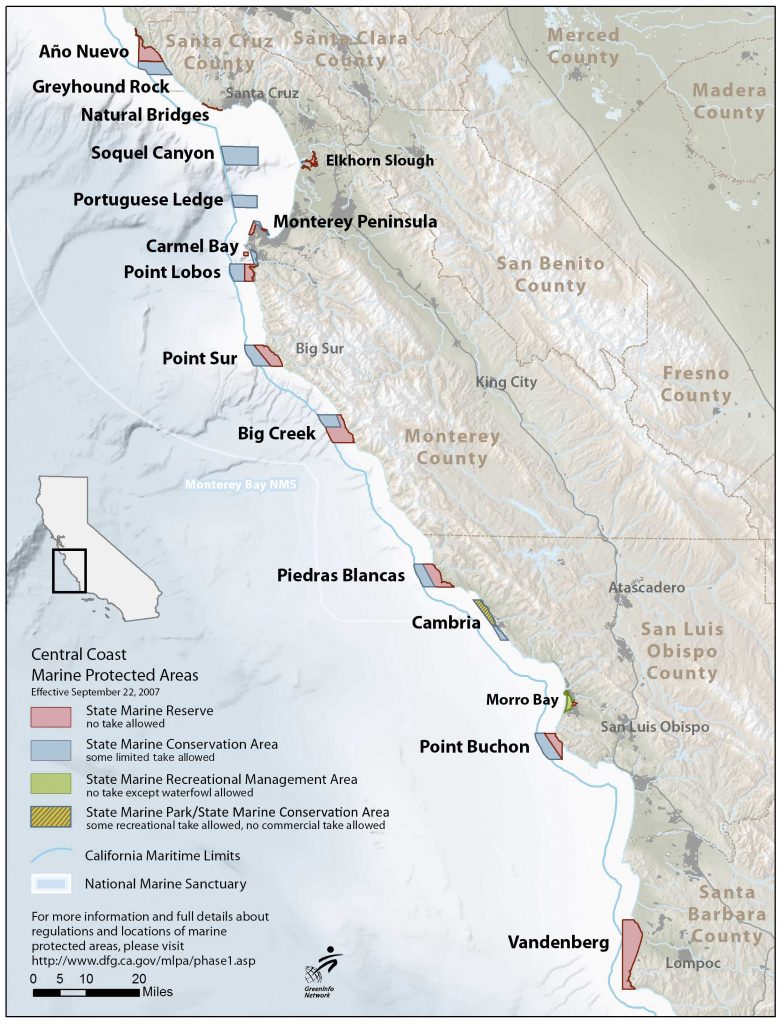
Central Coast
Twenty-nine MPAs were designated along the central coast between Pigeon Point in the north and Pt. Conception in the south. These became effective in September of 2007. MPAs in this study region include 13 SMRs, 14 SMCAs, 1 SMP, and 1 SMRMA. The MPAs cover 18% of state waters, with 7.5% being no-take state marine reserves.
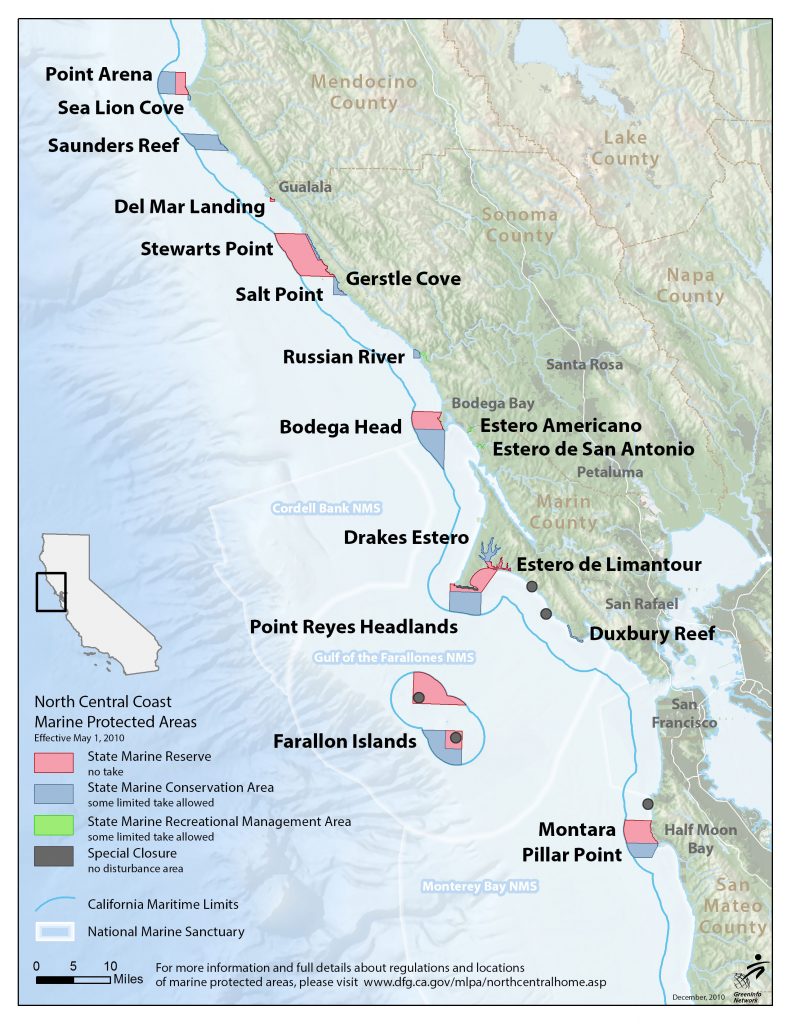
North Central Coast
Twenty-five MPAs and 6 special closure areas were designated in the north central coast, between Alder Creek near Point Arena in the north and Pigeon Point in the south. These became effective in May of 2010. MPAs in this study region include 10 SMRs, 12 SMCAs, and 3 SMRMA. The MPAs cover 20% of state waters, with 11% being no-take state marine reserves.
North Coast
Twenty MPAs and 7 special closure areas were designated in the north coast, between the California/Oregon border in the north and Alder Creek near Point Arena in the south. These became effective in December 2012. MPAs in this study region include 6 SMRs, 13 SMCAs and 1 SMRMA.
South Coast
Fifty MPAs and 2 special closure areas were designated in the south coast, between Point Conception in the north and the Mexican border in the south, including offshore islands. These became effective in January 2012. MPAs in this study region include 19 SMRs, 10 no-take SMCAs, and 21 SMCAs.
San Francisco Bay
Planning for the San Francisco Bay Study Region is currently on hold. This is the fifth and final study region for consideration under the Marine Life Protection Act (MLPA) and would include waters within San Francisco Bay, from the Golden Gate Bridge northeast to the Carquinez Bridge. To see a list of current MPAs within San Francisco Bay, please click the link below.